Introduction to Automation in Modern Mills
The integration of automation in modern mills has revolutionized the way milling operations are conducted. With advancements in technology, mills have transitioned from manual operations to highly efficient, automated systems. This change has led to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved product quality.
The Role of Automation in Milling
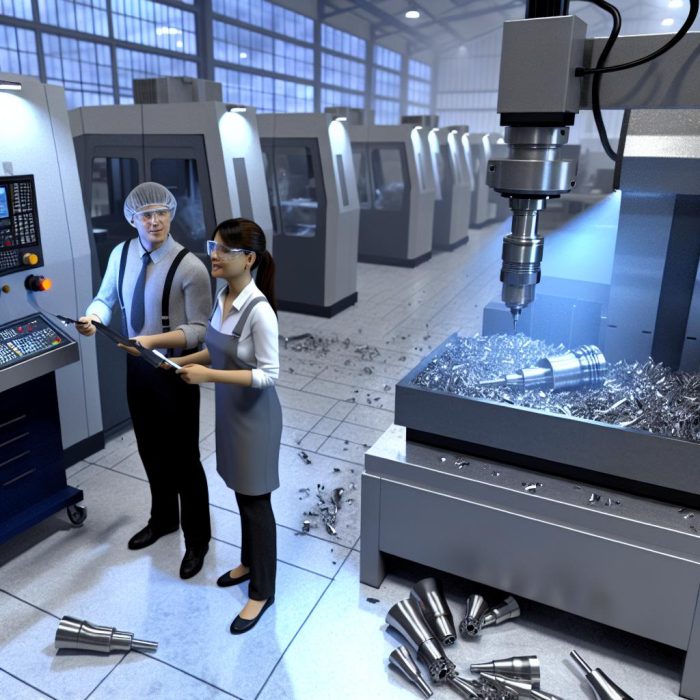
Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining processes in mills. Automated systems manage various stages of milling, from the raw material intake and processing to the packaging of finished products. These systems are designed to operate with minimal human intervention, utilizing sophisticated software and machinery to ensure precise and consistent outputs.
Key Technologies in Mill Automation
One significant technology impacting modern mills is the implementation of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). PLCs are essential for controlling mechanical processes, facilitating communication between different parts of the mill, and ensuring efficient operation. Additionally, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems monitor mill activities in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments to optimize performance.
Moreover, the use of sensors and actuators helps in maintaining quality by monitoring product characteristics and equipment performance. These technologies ensure that the production process is both efficient and flexible, adapting to different types and grades of materials.
Benefits of Automation in Mills
The shift to automated systems offers several benefits. First, automation enhances productivity by enabling mills to operate continuously without the downtime associated with manual human operations. This continuous operation significantly increases output and decreases the time required to meet production targets.
Additionally, automation reduces labor costs. By minimizing the need for manual operations, mills can operate with fewer personnel, redirecting human resources to more strategic roles such as oversight and quality control. Another advantage is the improvement in product consistency and quality. Automated systems can maintain strict control over the process parameters, thus minimizing human error and ensuring a consistent end product.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, implementing automation in mills comes with challenges. Mills must invest in training personnel to manage and maintain these sophisticated systems. Additionally, the initial investment in automation technology can be substantial, although it is often offset by the long-term savings and productivity gains.
Furthermore, mills must consider data security and ensure that their systems are protected from potential cyber threats. With the integration of Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring secure and reliable communication becomes crucial.
Looking Ahead
The future of automation in milling is promising, with ongoing research into further advancements such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies aim to create even smarter and self-optimizing mills, capable of adapting to new challenges and opportunities in the industry.
For more information and detailed studies on the impact of automation in mills, you can visit Industry News Resource.
Exploring the Transition to Fully Automated Mills
As the milling industry progresses towards full automation, the transition involves substantial changes not just in machinery but also in operational mindsets. The move towards a digital future requires overcoming technical and managerial challenges, embarking on a journey that demands highly technological investments and strategic planning.
Adapting to Digital Platforms
Adopting digital platforms in mill operations is essential as the industry migrates from conventional systems to automated frameworks. Digital platforms offer integrated solutions combining hardware with software, allowing mills to achieve optimized process flows and data-driven decision-making capabilities.
Mill operators are benefiting from digital dashboards that provide real-time insights into production efficiencies, resource utilization, and overall equipment effectiveness. The use of digital tools coupled with automation creates an interconnected environment that facilitates proactive maintenance and minimizes operational disruptions.
Transforming Workforce Dynamics
With the surge in automation, the workforce dynamics within mills are transformed significantly. The need for traditional manual skills is gradually diminishing, creating a demand for a workforce that is adept in technology-driven operations. To accommodate these shifts, mills must focus on workforce training, equipping employees with skills such as data analysis, systems management, and maintenance of automated equipment.
By investing in a technologically savvy workforce, mills not only improve operational efficiency but also ensure that employees are prepared for the technological demands of the future. The transformation of workforce dynamics is a crucial element in the seamless transition to automated milling processes.
Enhancing Efficiency Through Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a strategic aspect of automation in mills. By adopting a culture of constant enhancement and optimization, mills can explore new methods to improve efficiency and reduce wastage at every production stage. Automation allows for detailed monitoring and analysis, providing insights that facilitate ongoing improvements in process and performance.
Incorporating feedback mechanisms and agile methodologies enables mills to adapt swiftly to market demands and technological advancements. Engaging in continuous improvement efforts leads to sustained growth, ensuring mills remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The shift towards automation in mills symbolizes a significant leap towards achieving industrial excellence in the milling sector. By integrating advanced technologies and focusing on continual adaptation and enhancement, mills are set to redefine standards in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
The journey to fully automated milling operations is complex and multifaceted, involving technological, managerial, and workforce-related changes. As mills embrace this digital transformation, they reinforce their commitment to innovation and pave the road for future advancements in the milling industry.
Ultimately, the integration of automation represents not only a shift in operations but a vision towards a future where milling processes are characterized by intelligence, agility, and resilience. For more updates and insights in the field of mill automation, industry professionals can find a wealth of information at Industry News Resource.