Introduction to Eco-Friendly Grain Milling
Grain milling serves as an essential component in the production of numerous food products. In this context, incorporating eco-friendly practices can play a pivotal role in enhancing environmental sustainability. The grain milling industry traditionally requires significant energy and resource consumption, which culminates in a considerable environmental impact. However, by integrating sustainable methodologies, it is possible to considerably alleviate this impact.
Sustainable Milling Technologies
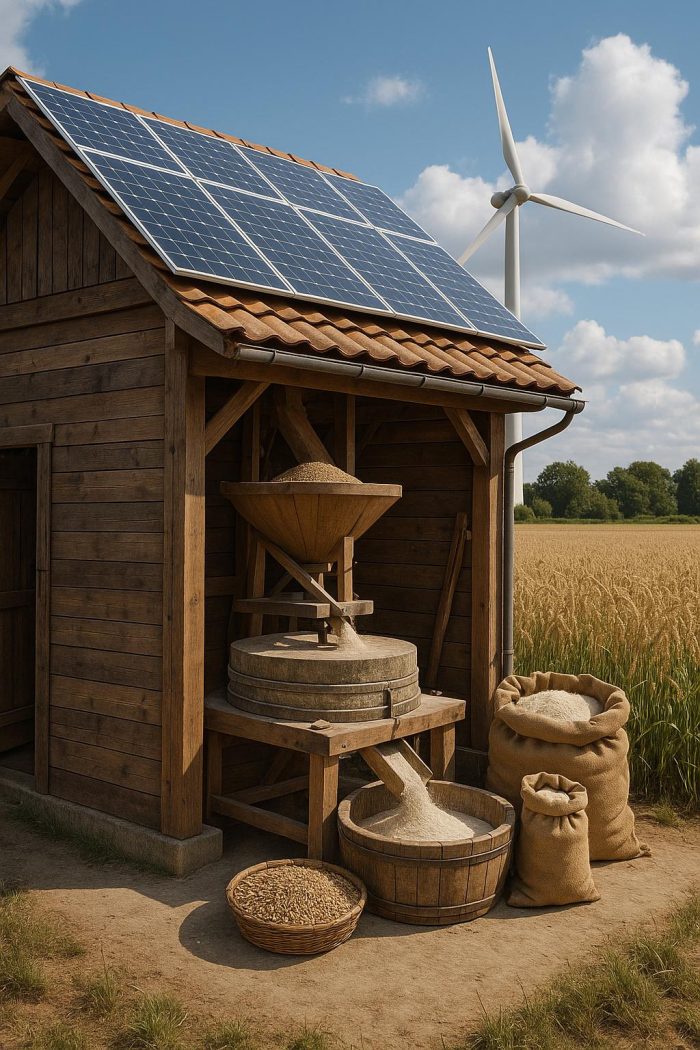
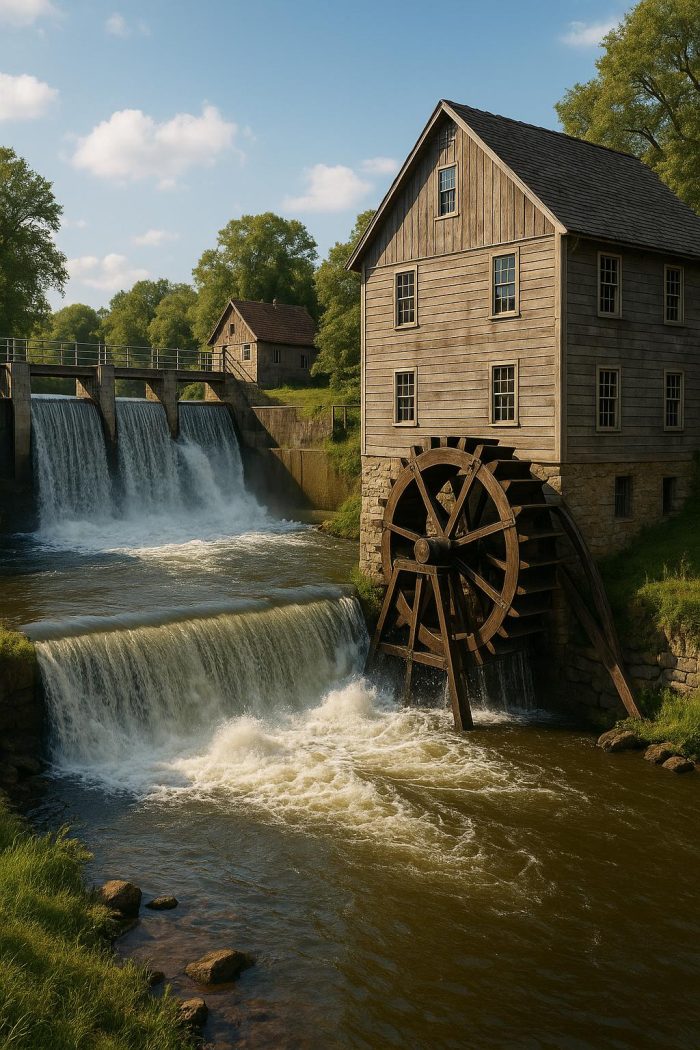
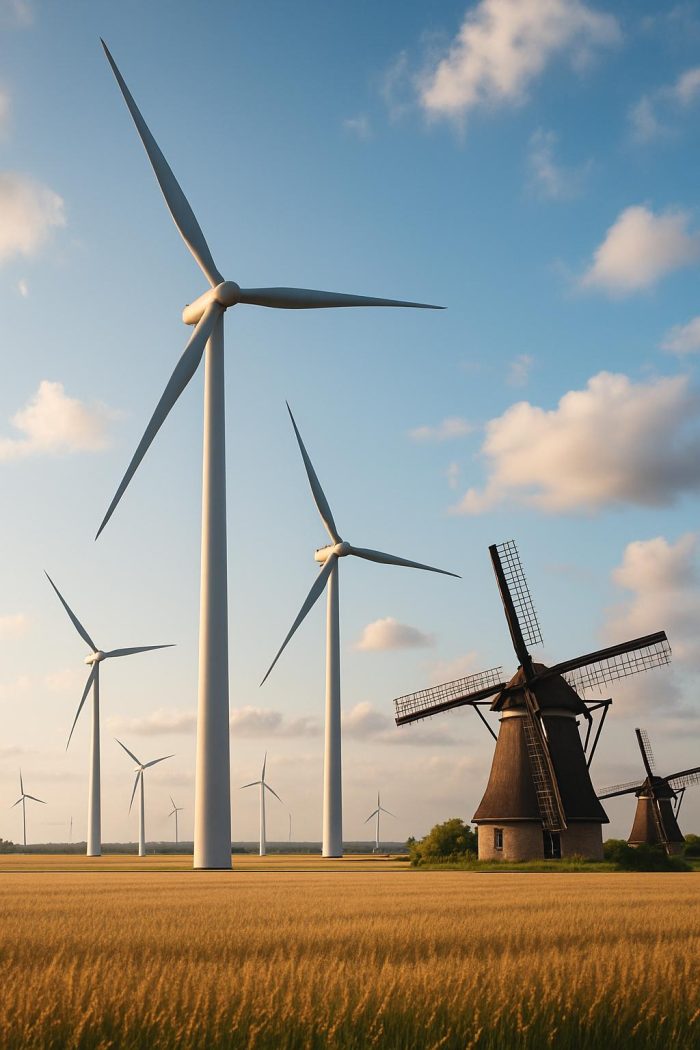
Modern technological advancements pave the way for sustainable milling methods that balance efficiency with environmental consciousness. A fundamental advance is the harnessing of renewable energy sources to power milling operations. Prominent among these sources are solar and wind energies, each offering a viable means to reduce the carbon footprint of milling facilities. Additionally, the employment of energy-efficient machinery is instrumental in diminishing energy consumption throughout the milling processes.
As technology has advanced, so too have the options available for creating more energy-efficient equipment. This includes the development of automated systems designed to optimize energy use, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and sustainably. Furthermore, by employing smart technologies, facilities can monitor energy consumption in real-time, identifying areas for improvement and making adjustments accordingly.
Water Conservation Techniques
Water usage remains a critical element in grain milling, particularly in procedures such as cleaning and conditioning. The implementation of closed-loop water systems serves to significantly reduce overall water usage. These systems work by cleaning and recycling the water within the facility itself, minimizing wastage. This conservation method not only helps in reducing water consumption but also allows facilities to maintain consistent quality in water used for milling processes.
Employing dry milling techniques wherever feasible further diminishes reliance on water. Dry milling is characterized by its ability to process grains without the addition of water, thereby conserving water resources while still delivering the desired product quality. By reducing water dependency, facilities can optimize resource use and lessen the strain on local water supplies.
Waste Management and By-product Utilization
The generation of waste is another significant issue in grain milling. Effective waste management strategies are indispensable in crafting operations that are environmentally conscientious. One promising strategy involves converting milling by-products such as bran and germ into supplementary products like animal feed or biofuel. This approach not only reduces waste generated by the milling process but also creates additional product streams that contribute to economic sustainability.
Moreover, waste separation and recycling are vital aspects of eco-friendly milling. By categorizing materials based on their recyclability, milling plants can effectively streamline the recycling process, ensuring that as much material as possible is reused or repurposed. This practice not only diminishes waste production but also yields further environmental benefits by reducing the demands placed on landfills.
Local Sourcing and Supply Chain Improvements
Minimizing the environmental impact of grain milling involves refining supply chain strategies. Procuring grains from local farmers reduces transportation emissions, supporting local economies while lowering the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transport. By prioritizing local sourcing, milling operations benefit from fresher produce and contribute to regional food systems.
Partnerships with suppliers that practice eco-friendly farming methods are another integral component in promoting sustainable grain supply chains. These partnerships ensure a holistic approach to sustainability wherein every link in the supply chain is committed to environmental preservation. Such collaborations enable continuous improvements in farm-to-table processes and support a broader commitment to sustainability across the industry.
This emphasis on local and sustainable sourcing not only benefits the environment but also helps to safeguard against disruptions in the global supply chain. By minimizing dependency on distant suppliers, the industry can maintain stability and resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges.
By incorporating these eco-friendly grain milling practices, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint without sacrificing efficiency and productivity. For further exploration of sustainable milling practices and technologies, engaging with resources from reputable environmental organizations and industry pioneers is recommended. These sources can offer critical insights and inspiration, driving continued innovation in eco-friendly grain milling. Through conscientious and committed efforts, the grain milling sector can achieve significant advancements in sustainability, benefiting both the environment and society at large.